In the digital era, where online privacy concerns and security threats loom large, the question “What is a VPN?” becomes more than just technical curiosity; it’s a crucial inquiry for safeguarding your digital life. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) offers a protective shield for your internet connection, encrypting your data and concealing your online activities from unwanted scrutiny. This blog post is your comprehensive guide to understanding VPNs—covering their importance, how they work, and how to choose the right one for your needs. Join us as we navigate the ins and outs of VPN technology, highlighting its pivotal role in enhancing your online privacy and security.
Table of Contents
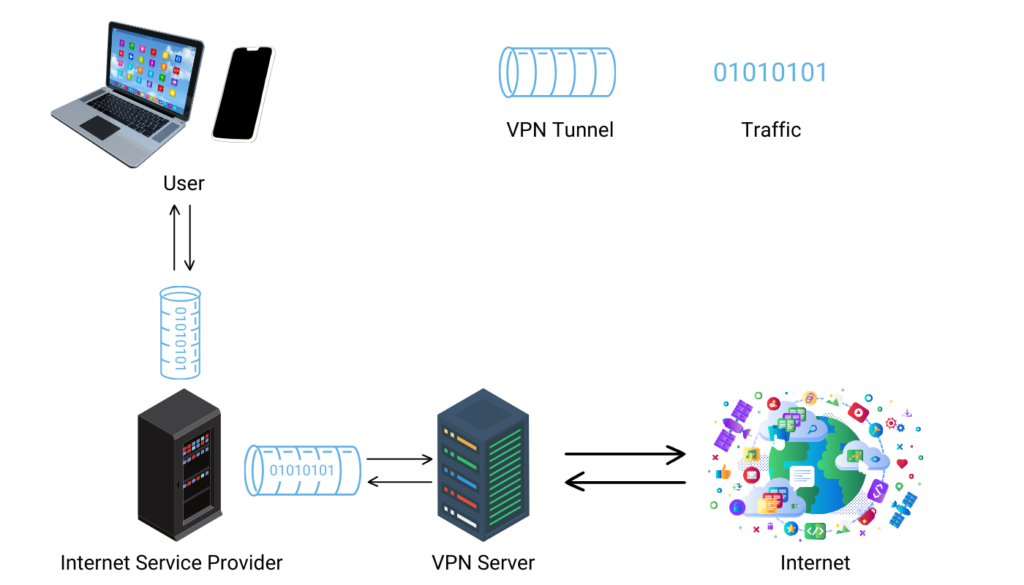
How VPNs Work
Understanding how VPNs work is essential for anyone looking to enhance their online security and privacy. At its core, a VPN establishes a private, encrypted tunnel for your internet data to travel through, shielding your information from prying eyes. When you connect to a VPN, it redirects your internet traffic through one of its servers located around the globe. This process changes your IP address and encrypts your data, making it seem as though your online activities are originating from the VPN server rather than your actual location.
The encryption used by VPNs is what sets them apart in terms of security. This encryption scrambles your data in such a way that it becomes unreadable to anyone who intercepts it. Even if a cybercriminal were to capture your data, decrypting it without the encryption key would be virtually impossible. This is particularly valuable when you’re using public Wi-Fi networks, known for their vulnerabilities and ease of access for hackers.
VPNs utilize various protocols to secure and encrypt your data, including OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, and WireGuard, each with its own strengths and suited for different use cases. The choice of protocol can affect the speed and security of your VPN connection, but the ultimate goal remains the same: to provide a secure and private online experience.
Key Features of VPNs
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) come equipped with several features designed to protect your online privacy and enhance your internet experience. Understanding these key features is crucial for anyone considering the use of a VPN to safeguard their digital life. Here’s a look at the most significant attributes of VPNs and how they contribute to your online security and freedom.
Encryption: The cornerstone of any VPN is its ability to encrypt your internet traffic. This means turning your data into a coded format that can only be deciphered with the correct key. High-level encryption, such as AES-256, ensures that your online activities, from banking transactions to browsing history, remain confidential.
IP Masking: A VPN conceals your real IP address by replacing it with one from its server network. This not only hides your location from websites, advertisers, and potentially malicious actors but also allows you to bypass geographical restrictions and censorship.
No-Logging Policy: Reputable VPN providers adhere to a strict no-logging policy, meaning they do not keep records of your internet activities. This feature is vital for maintaining your privacy, as it ensures that even your VPN provider cannot track or share your online movements.
Kill Switch: This safety feature automatically disconnects your device from the internet if the VPN connection drops, preventing your data from being exposed. It’s an essential fail-safe that ensures continuous protection of your online activities.
Split Tunneling: Split tunneling allows you to choose which apps or websites go through the VPN tunnel and which connect directly to the internet. This can optimize your connection speed and allow for more control over your online privacy.
Server Locations: The number and distribution of servers in a VPN’s network can significantly impact your internet speed and the ability to access content from different regions. A wide selection of servers gives you more options for geo-spoofing your location.
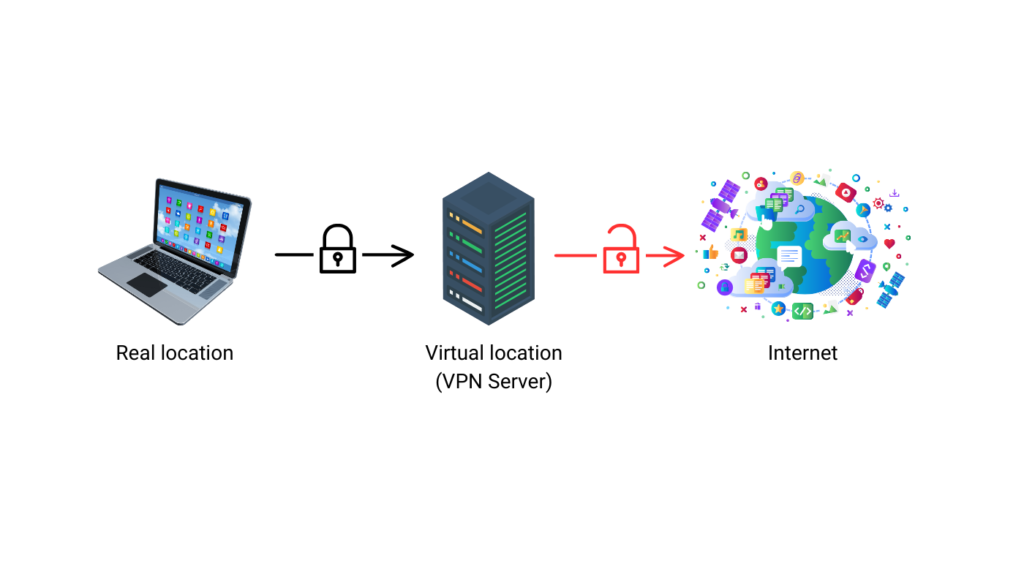
How encryption works
Pros and Cons of Using a VPN
Utilizing a VPN can significantly enhance your online experience by providing privacy, security, and freedom. However, like any technology, VPNs come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here, we’ll explore the pros and cons of using a VPN, helping you make an informed decision about incorporating this tool into your digital life.
Pros of Using a VPN:
- Enhanced Privacy and Security: The primary advantage of a VPN is its ability to secure your internet connection by encrypting your data. This makes it nearly impossible for hackers, ISPs, or government agencies to monitor your online activities or steal your information.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: VPNs allow you to access content from anywhere in the world by changing your IP address. Whether it’s streaming services, news websites, or gaming platforms, you can bypass geo-restrictions and censorship.
- Safe Use of Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks are notorious for their security vulnerabilities. A VPN protects your data on these networks, ensuring that your personal information remains private and secure.
- No Bandwidth Throttling: ISPs sometimes throttle bandwidth based on your internet activities. A VPN hides your online activities, helping prevent ISPs from throttling your internet speed.
Cons of Using a VPN:
- Potential Slowdown in Internet Speed: Encryption and routing your data through a VPN server can sometimes slow down your internet speed, especially if the server is far away or overcrowded.
- Complexity for Novice Users: Setting up and optimizing a VPN might be challenging for less tech-savvy individuals, although many providers strive to make their software user-friendly.
- Cost: While there are free VPN options, they often come with limitations in speed, data, and security. Premium VPN services provide comprehensive features but at a cost.
- Legal and Policy Considerations: The legality of VPN use varies by country. Some countries have restrictions or outright bans on VPN usage, so it’s essential to be aware of local laws and VPN policies.

Common Use Cases for VPNs
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are versatile tools that serve a variety of purposes beyond just encrypting your internet traffic. Whether you’re a casual internet user, a remote worker, or a global traveler, understanding the common use cases for VPNs can help you make the most of this powerful technology. Here are some scenarios where a VPN becomes particularly useful:
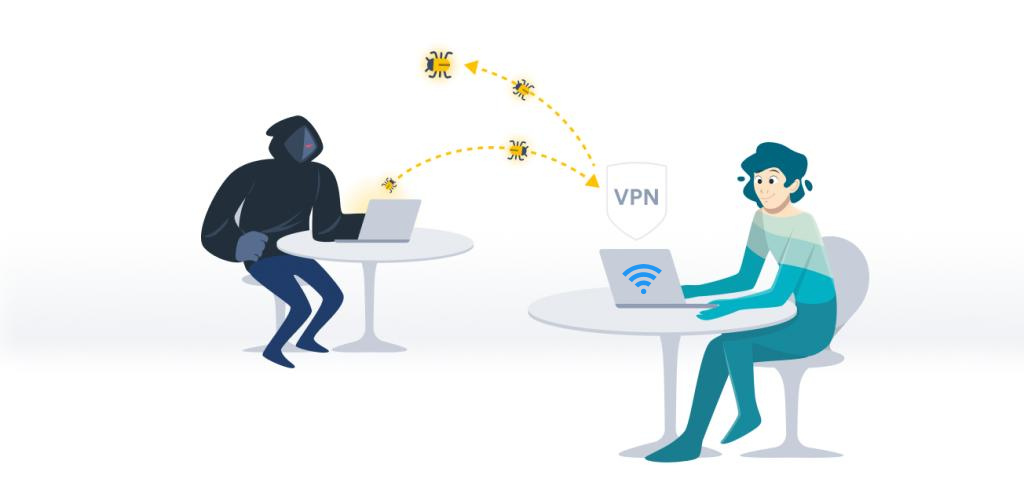
1. Securely Accessing Public Wi-Fi: One of the most common reasons to use a VPN is to secure your internet connection when using public Wi-Fi networks, such as those in coffee shops, airports, or hotels. These networks are often unsecured, making them a hotspot for cybercriminals looking to intercept data. A VPN encrypts your online activities, protecting your personal information from potential threats.
2. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions and Censorship: Whether you’re trying to access region-locked content on streaming services or facing internet censorship in certain countries, a VPN can help. By connecting to a server in a different location, you can bypass geo-restrictions and censorship, accessing the internet freely and without limitations.
3. Safeguarding Privacy from ISPs and Advertisers: Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see and track your online activities, potentially throttling your bandwidth based on the content you access. Moreover, advertisers often use your location and browsing history to target ads. A VPN hides your activity and location, keeping your browsing habits private from ISPs and advertisers.
4. Remote Access to Work Resources: For remote workers and businesses, VPNs provide a secure way to access work networks and resources from anywhere in the world. This is particularly important for accessing sensitive corporate data or performing tasks on a secure network.
5. Protecting Sensitive Transactions: Whether you’re online banking, shopping, or dealing with sensitive information, a VPN ensures that your transactions are secure and private. This is crucial for preventing identity theft and financial fraud.
Choosing the Right VPN
Selecting the right VPN can significantly impact your online security, privacy, and overall internet browsing experience. With numerous VPN services available, it’s crucial to understand the factors that distinguish one VPN from another. Here are key considerations to keep in mind when choosing the right VPN for your needs:
1. Security Features: The primary purpose of a VPN is to secure your online activities. Look for VPNs that offer strong encryption standards (such as AES-256), a range of secure protocols (like OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, or WireGuard), and features like a kill switch, which ensures your data remains protected even if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly.
2. Privacy Policy: A trustworthy VPN provider should have a strict no-logs policy, meaning they do not keep any records of your online activities. This is crucial for ensuring that your browsing habits, location, and personal data remain private, even from the VPN provider itself.
3. Speed and Performance: Since VPNs encrypt your data and route it through their servers, they can sometimes slow down your internet connection. Test the speed of different VPN services to ensure they meet your needs, especially if you plan on streaming, gaming, or downloading large files.
4. Server Locations: The number and distribution of a VPN’s servers can affect your connection speed and your ability to access content from specific regions. Consider VPNs with a wide range of server locations, particularly if you’re looking to bypass geo-restrictions or censorship.
5. Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is important, especially for those not technically inclined. Look for VPNs that offer easy-to-use apps for all your devices, ensuring you can securely connect to the VPN without hassle.
6. Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential, particularly if you encounter issues with your VPN connection. Check for VPNs that provide 24/7 support through live chat or email, offering peace of mind that help is available when you need it.
7. Price: While free VPNs are tempting, they often come with limitations in speed, security, and features. Evaluate the pricing of various VPNs, considering both monthly and annual subscription plans, to find a service that offers the best value for your budget.
Setting Up a VPN
Setting up a VPN is a straightforward process that can significantly enhance your online privacy and security. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or new to the concept, understanding the steps involved in setting up a VPN is crucial. Here’s a simple guide to get you started, ensuring you can navigate this setup with ease.
1. Choose a Reliable VPN Provider: Start by selecting a VPN provider that meets your needs, taking into consideration factors like security features, server locations, and privacy policies. Once you’ve chosen a provider, sign up for an account on their website.
2. Download and Install the VPN App: After signing up, download the VPN application for your device from the provider’s website or a trusted app store. Follow the installation instructions specific to your operating system (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, etc.).
3. Log In and Connect to a Server: Open the VPN app and log in using the credentials you created during sign-up. Most VPN apps feature a quick-connect option that automatically selects the best server for you. Alternatively, you can manually select a server location based on your specific needs, such as bypassing geo-restrictions or seeking faster connection speeds.
4. Configure Your VPN Settings (Optional): Explore the app’s settings to customize your VPN experience. This may include selecting a VPN protocol, enabling a kill switch for added security, or setting up split tunneling to decide which apps use the VPN connection.
5. Test Your VPN Connection: Once connected, it’s a good idea to test your VPN to ensure it’s working correctly. You can check your IP address using a service like WhatIsMyIP.com to confirm that your actual location is hidden. Additionally, running a speed test can help you gauge the impact of the VPN on your internet connection.
VPN app interface
Free vs. Paid VPNs
Free VPNs:
Free VPN services are attractive because they offer basic VPN features without a financial commitment. However, they often come with significant limitations:
- Data Limits: Many free VPNs impose data caps, restricting how much data you can use while connected to the VPN. This can be a major drawback for activities like streaming or downloading.
- Speed Throttling: To manage server load, free VPNs may throttle your internet speed, leading to slower browsing, streaming, and downloading speeds.
- Limited Server Options: Free VPNs typically offer a limited number of servers, which can lead to overcrowded servers and further reduce speeds.
- Privacy Concerns: Some free VPNs may log your browsing activities or serve ads, raising concerns about how your data is used and potentially undermining the privacy protection VPNs are meant to provide.
Examples of Free VPN Services:
- ProtonVPN: Offers unlimited data but with speed limitations and a limited number of servers.
- Windscribe: Provides a generous data allowance compared to other free VPNs, with additional features available for premium accounts.
Paid VPNs:
Investing in a paid VPN service generally offers a more comprehensive and secure online experience:
- Unlimited Data: Most paid VPNs provide unlimited bandwidth, allowing for uninterrupted streaming, downloading, and browsing.
- Higher Speeds: Paid VPNs invest in high-quality servers and infrastructure, offering faster connections and higher speeds.
- Advanced Security Features: Features like kill switches, advanced encryption protocols, and no-logs policies are standard with many paid VPNs, offering superior security and privacy.
- Global Server Networks: Access to a wide array of servers worldwide, enabling you to bypass geo-restrictions more effectively and access a broader range of content.
Examples of Paid VPN Services:
- NordVPN: Known for its strong security features, extensive server network, and fast speeds. You can also familiarize yourself with the comparison of NordVPN and IPVanish in our article.
- ClearVPN: Offers a user-friendly interface, fast speeds, and servers in 94 countries.
- Surfshark: Provides unlimited device connections, strong privacy policies, and a wide range of security features at a competitive price.
VPN and Legality
The legality of using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) varies significantly across the globe, making it essential for users to understand the legal context of VPN usage in their country or any region they intend to use it. While VPNs are legal in most countries because of their importance in enhancing online security and privacy, there are exceptions and specific regulations you should be aware of.
Where VPNs are Generally Legal: In countries like the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia, VPNs are legal. They’re widely used by individuals and businesses alike for securing their internet connection, protecting their data, and bypassing geo-restrictions on content.
Countries with Restrictions on VPN Use: Some countries have imposed restrictions on VPN use, usually for reasons related to national security, to enforce censorship, or to control the flow of information. These restrictions often require VPN services to be licensed or approved by the government, or they may ban the use of non-approved VPNs altogether. Countries with such restrictions include China, Russia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates.
Where VPN Use is Illegal: In a few countries, the use of VPNs is outright illegal unless specifically allowed for government or corporate use. The legal penalties for using a VPN in these countries can range from fines to imprisonment, depending on the country’s laws and the context of the VPN use.
Considerations for Using a VPN Legally:
- Abiding by Local Laws: Always check the current laws regarding VPN use in your country or any country you’re visiting. Legal standards can change, and staying informed is crucial.
- Ethical Use: Even in countries where VPNs are legal, using a VPN for illegal activities, such as hacking, accessing illegal content, or committing fraud, is punishable under the law.
- Corporate Use: In some regions, using a VPN for personal privacy or security is restricted, but companies can legally use them for securing corporate data and communications.
Future of VPN Technology
The future of VPN technology promises to be dynamic and innovative, driven by evolving cybersecurity threats, technological advancements, and changing user needs. As digital privacy concerns and geo-restrictions continue to grow, VPNs are becoming increasingly essential for both individual users and businesses. Here’s what the future holds for VPN technology, emphasizing key trends and developments.
Increased Adoption and Demand: As awareness of online privacy issues grows, so does the adoption of VPNs. Individuals seek to protect their personal data, and businesses require secure connections for remote work. This rising demand will likely drive further innovation in VPN technologies and services.
Enhancements in Encryption Methods: Future VPNs are expected to adopt more advanced encryption algorithms to counter sophisticated cyber threats. Quantum-resistant encryption methods may become standard to prepare for the eventual arrival of quantum computing, which could render current encryption techniques vulnerable.
Improvement in Speed and Performance: The common critique of VPNs slowing down internet speed is being addressed with newer protocols that optimize speed without compromising security. Protocols like WireGuard® are already making strides in offering faster connections and better performance, a trend that is expected to continue.
Greater Integration with Internet of Things (IoT): As the number of IoT devices increases, so does the need to secure them. Future VPNs will likely offer more comprehensive solutions for protecting entire networks of smart devices, ensuring that all data transmitted is secure and private.
More User-friendly Features: VPNs will continue to evolve to be more accessible to the general public, with user-friendly interfaces and features that cater to less tech-savvy individuals. This includes automatic security features, such as auto-connect options and more intuitive settings management.
Adoption of Zero-Trust Security Models: With the shift towards remote work and cloud services, VPNs will integrate more deeply with zero-trust security models. This means continuous verification of all users and devices, offering a more secure and flexible approach to access management.
FAQs about What is a VPN
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are a pivotal component of online privacy and security, yet many users have questions about how they work and when to use them. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about VPNs, designed to clarify common concerns and misconceptions.
What is a VPN and how does it work? A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a service that encrypts your internet connection and reroutes it through a server in a location of your choice. This process hides your IP address, making your online actions more anonymous and securing your data from hackers and surveillance.
Is using a VPN legal? In most countries, using a VPN is perfectly legal. VPNs are widely used for legitimate purposes, such as enhancing online security and privacy. However, the legality of VPN use can vary by country, with some nations imposing restrictions or outright bans, so it’s essential to check the laws in your jurisdiction.
Can VPNs be tracked? While a VPN hides your IP address and encrypts your data, making it much harder to track your online activities, it’s not entirely untraceable. Advanced techniques and resources, like those possessed by government agencies, can potentially track VPN use. However, for the average user, a VPN provides a significant level of privacy and security.
Do VPNs slow down internet speed? VPNs can sometimes slow down your internet speed due to encryption and the distance your data travels to the VPN server. However, the impact is often minimal with premium VPNs that offer fast servers and advanced technology like the WireGuard® protocol.
Should I always use a VPN? Using a VPN is especially recommended when you’re on public Wi-Fi, accessing sensitive information, or browsing in countries with strict internet censorship. However, for general browsing at home, the necessity of a VPN depends on your privacy concerns and specific online activities.
Can I use a free VPN? While free VPNs are available, they often come with limitations like data caps, slower speeds, and fewer server options. Some free VPNs may also compromise your privacy by tracking your activities or displaying ads. For comprehensive protection and a better experience, a paid VPN service is usually recommended.
Conclusion
Navigating the vast and ever-evolving digital landscape requires not only awareness but also the right tools for ensuring your online security and privacy. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) stand out as one of the most effective and versatile tools in the digital age, offering a blend of security, privacy, and freedom that is hard to match with any other single technology.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored what VPNs are, how they work, their key features, and the pros and cons of using them. We’ve delved into common use cases, guiding you through choosing the right VPN, setting it up, and understanding the differences between free and paid services. Legal considerations, the future of VPN technology, and answers to frequently asked questions have been covered to give you a well-rounded understanding of VPNs and their significance.
A VPN is a crucial ally in the journey towards a safer and more private online experience, addressing a wide range of online privacy and security issues such as protecting personal data, bypassing geo-restrictions, and securing internet connections.






Pingback: Surfshark VPN Review 2024: Unmatched Security Explored - IndieSoftReview
Pingback: Best VPN 2024: Surfshark vs NordVPN - IndieSoftReview
Pingback: Dominica VPN – Your Ultimate Guide to Internet Freedom and Security 2024 - IndieSoftReview
Pingback: El Salvador VPN: Essential for Secure and Open Internet Access 2024 - IndieSoftReview
Pingback: VPN for Argentina: 3 Best Providers for Secure Browsing!” - IndieSoftReview
Pingback: ExpressVPN vs IPVanish: Strong Contender or Clear Winner 2024? - IndieSoftReview